TRENDING
Tourist Destinations Disappearing Before Our Eyes
Published
3 years agoon
In an ever-changing world, the sights and scenery around us are just as capable of evolution and decay as we humans are. While there’s always more modern engineering achievements being built, there are a bunch of natural, historical, and iconic places that are under threat. And not only from environmental factors like climate change or erosion, but tourism and geopolitical conflict, too.
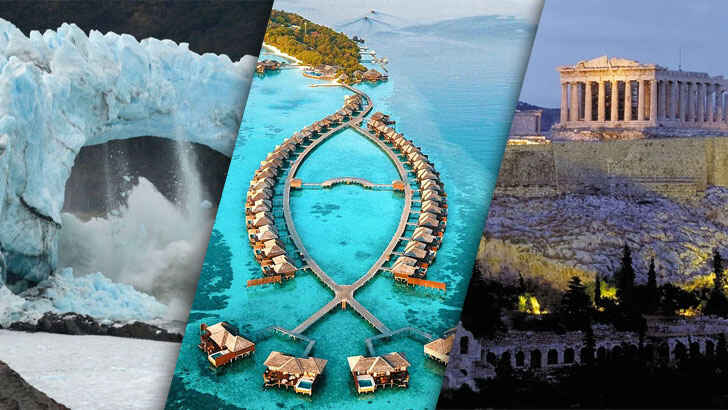

Whether humans built these places or not, there’s no arguing that the number of visitors, conflict, vandalism, and unfortunate environmental circumstances directly lead to the declining conditions of these popular world sites. We hope the money from visitors is directly invested into preserving the area, but is it too late? Now you must decide – are you one who wants to visit before they’re gone, or stay away in hopes that they’ll survive longer? How many have you been to?
Old U.S. Mint
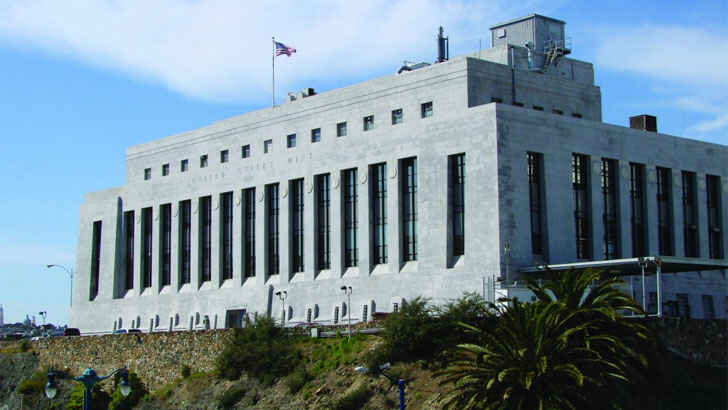

The San Francisco U.S. Mint is a branch of the United States Mint that was established in 1854 to serve the gold mines of the California gold rush, and it continued to produce coins for circulation and commemorative medals for years. Now, it sadly sits unused despite still being a popular tourist attraction, however the tech industry continues to build around it, surely making its days numbered
Jiuzhaigou
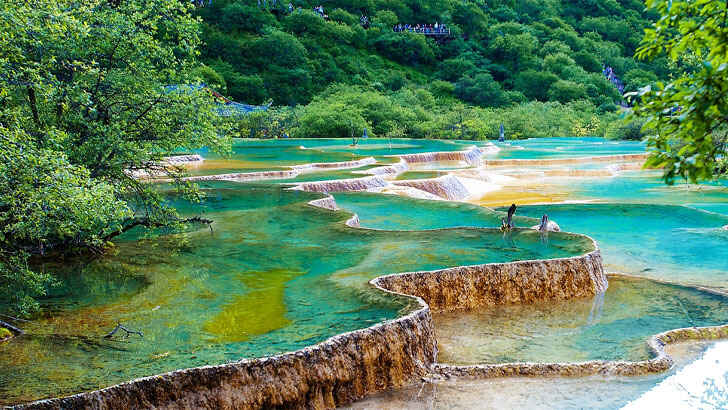

Jiuzhaigou, also known as Jiuzhai Valley, is a national park located in the northern part of Sichuan province in China. The park is known for its breathtaking scenery, which includes a series of crystal-clear lakes, waterfalls, and forests. The area is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including many endangered species. Jiuzhaigou is also a popular tourist destination, and it was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1992. However, with over 1 million people visiting a year, the deterioration has become noticeable.
Grand Canyon
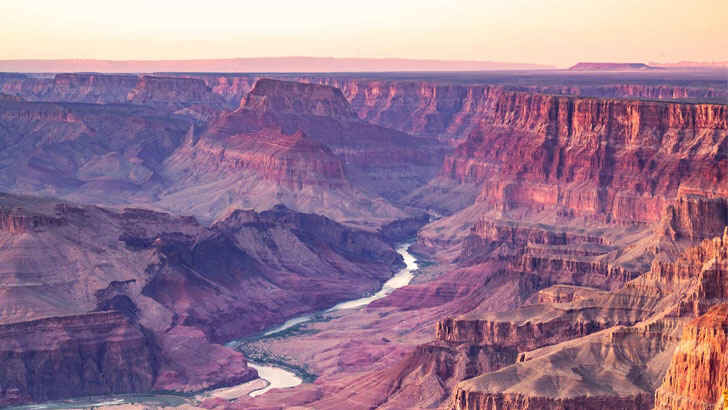

The Grand Canyon is known for its stunning views and unique geology, with layers of rock and sediment that reveal the Earth’s history. It is also home to a diverse array of plants and animals, and is a popular destination for hikers, climbers, and sightseers. And despite being a UNESCO World Heritage Site, recognized for its natural beauty and importance as a geological and ecological preserve, the amount of building, tourism, and mining in the area have shown there may be a new priority other than just the natural beauty of the canyon.
Taj Mahal
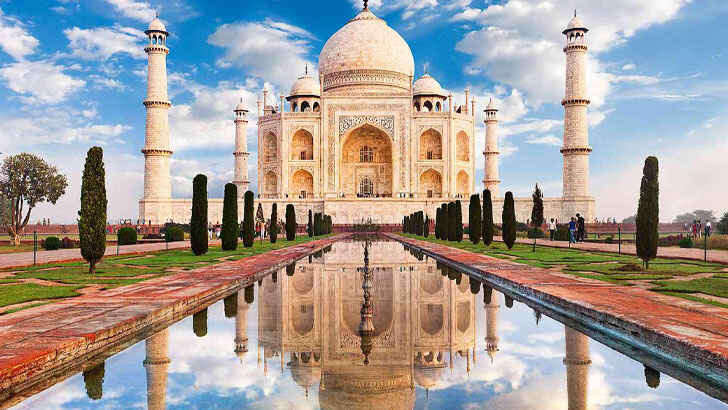

The Taj Mahal is a mausoleum located in Agra, India built by the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his favorite wife, Mumtaz Mahal, who died during childbirth. It’s widely considered one of the most beautiful buildings in the world, and is made of white marble and is adorned with intricate carvings and inlaid with precious stones. However, even with more than 40,000 visitors a day, it lacks the care it needs and is even affected by pollution. The Indian Supreme Court has even threatened to demolish the building if extensive changes aren’t made.
Great Barrier Reef
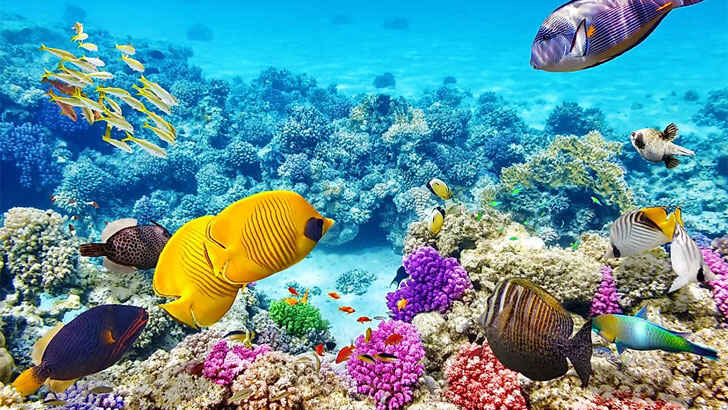

The Great Barrier Reef is the world’s largest coral reef system, comprising more than 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands that stretch for over 1,400 miles. The reef is home to a staggering array of marine life, including more than 1,500 species of fish, 411 species of hard coral, and numerous species of turtles, dolphins, and whales. It is also an important economic resource for the region, supporting tourism and fishing industries. However, the reef is facing significant threats from climate change, pollution, and overfishing, which have led to significant declines in the health and resilience of the ecosystem.
Dead Sea
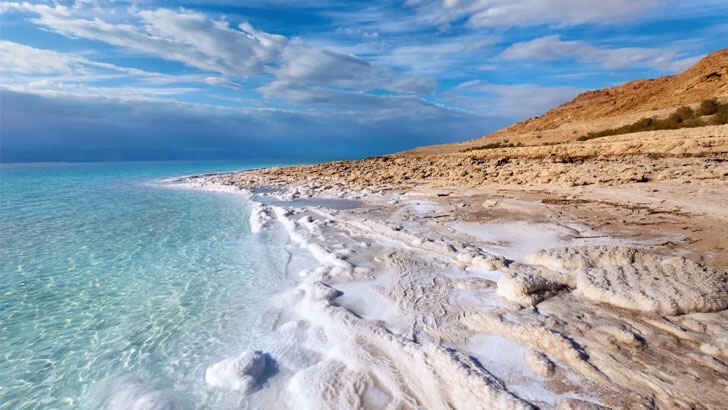

The Dead Sea is a salt lake located in the Jordan Rift Valley, between Israel and Jordan. It is the lowest point on land on Earth, with a surface elevation of about 1,412 feet below sea level. The Dead Sea is famous for its high salt content, and the water is so salty that it is unable to support plant or animal life, hence its name. The lake is fed by the Jordan River, but has no outflow, leading to the accumulation of salt and minerals in its water. The Dead Sea is facing environmental challenges, including the decreasing water level due to the overuse of its water resources and the impact of climate change.
Rainforests of Atsinanana
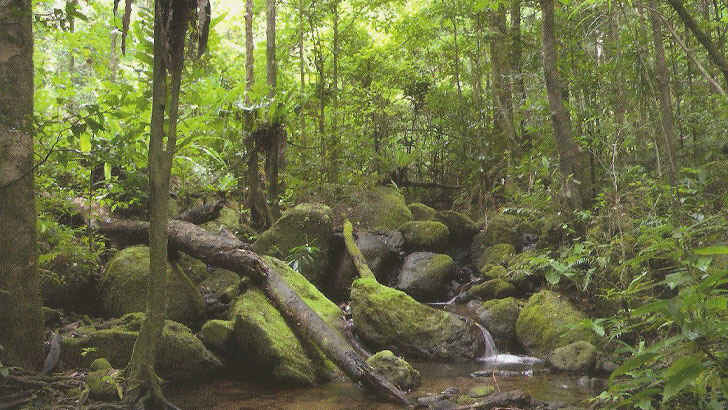

Atsinanana is a region in eastern Madagascar that is home to a number of protected rainforests. These forests are home to a rich and diverse array of plant and animal life, including many species that are found nowhere else on Earth. The rainforests are facing significant threats from logging, agriculture, and mining, which have led to the destruction of large areas of forest. Efforts are being made to protect and preserve these important ecosystems, including the establishment of protected areas and the promotion of sustainable land use practices.
Palmyra
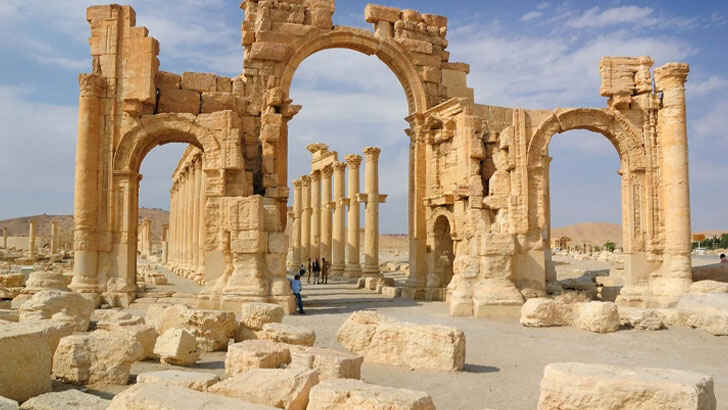

Palmyra is an ancient city located in modern-day Syria, in the Syrian Desert. Palmyra was a key city on the Silk Road, and was a major center of trade in the ancient world. The city was home to a number of important structures, including the Temple of Bel, the Agora, and the Great Colonnade, which were adorned with ornate carvings and decorations. Palmyra was also known for its sophisticated water management systems, which allowed the city to thrive in a desert environment. In recent years, Palmyra has been the site of significant cultural and political conflict, with the city being occupied and damaged by various groups during the Syrian civil war.
A.G. Gaston Motel
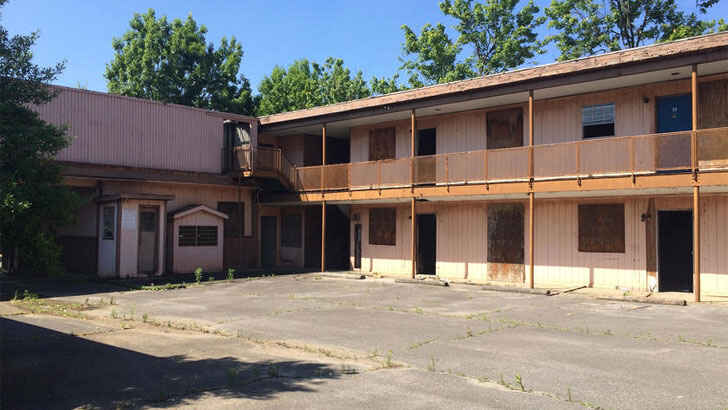

The A.G. Gaston Motel was a historic civil rights-era motel located in Birmingham, Alabama. It was owned by African American entrepreneur A.G. Gaston and served as a hub for the civil rights movement in the 1960s. The motel was a popular gathering place for civil rights leaders, including Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., and was the site of numerous strategy meetings and planning sessions during the civil rights movement. The motel also served as a safe haven and was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1982. However, with no renovation plans solidified, the hotel continues to deteriorate and be subject to vandalism.
Timbuktu
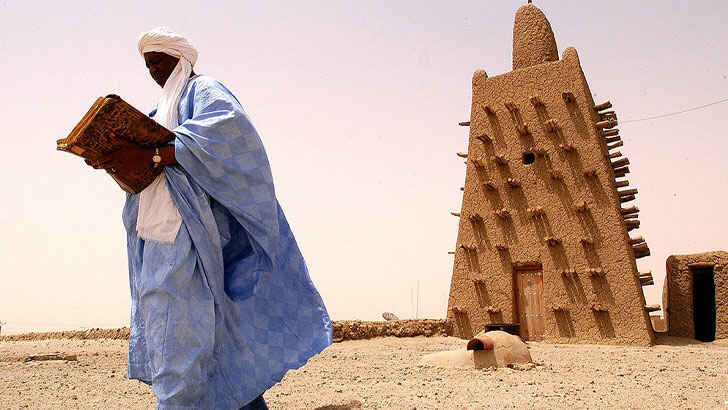

Timbuktu is a city in Mali, West Africa, that has a long and rich history dating back to the 5th century. It was once a major center of trade and intellectual activity, and was known for its universities and libraries. The city was also home to a number of important Islamic scholars and theologians, who contributed to the development of Islamic thought and culture. Today, Timbuktu is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is known for its historic mud brick architecture and cultural significance. However, the city has faced challenges in recent years due to conflict and instability in the region, especially from extremist groups.
Petra
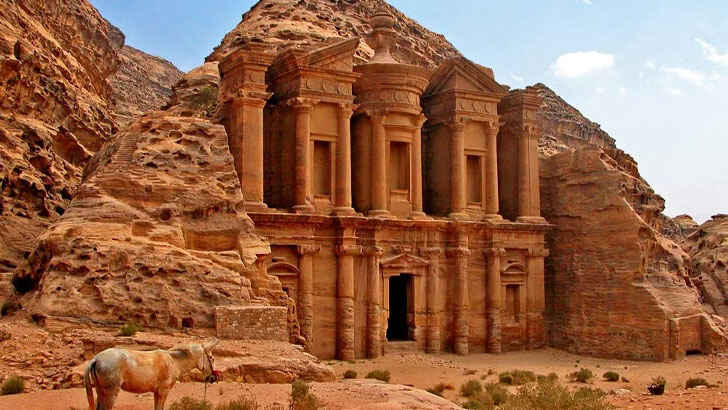

Petra is an ancient city located in modern-day Jordan. It is known for its stunning rock-cut architecture, which was carved into the red sandstone cliffs of the region. Petra is believed to have been founded in the 6th century BC and the city was a key stop on the Incense Route, a network of trade routes that connected Arabia, Africa, and the Mediterranean. Petra was home to a number of impressive structures, and today, Petra is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a popular tourist destination. However, erosion is quickly becoming an issue of preservation.
Kosovo Monasteries & Church
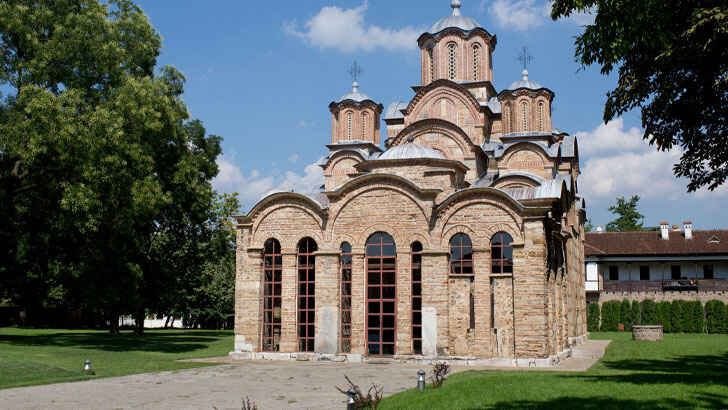

Many of Kosovo’s monasteries and churches were built during the medieval period and are examples of Byzantine and Ottoman-influenced architecture. Some of the most famous monasteries and churches in Kosovo include the Gračanica Monastery, the Patriarchate of Peć, and the Church of Our Lady of Ljeviš, which are all UNESCO World Heritage Sites. These religious buildings are important centers of faith and cultural traditions for the country’s predominantly Orthodox Christian population, but the lack of upkeep and numerous decades of political instability are pushing these buildings to their demise.
Mount Kilimanjaro
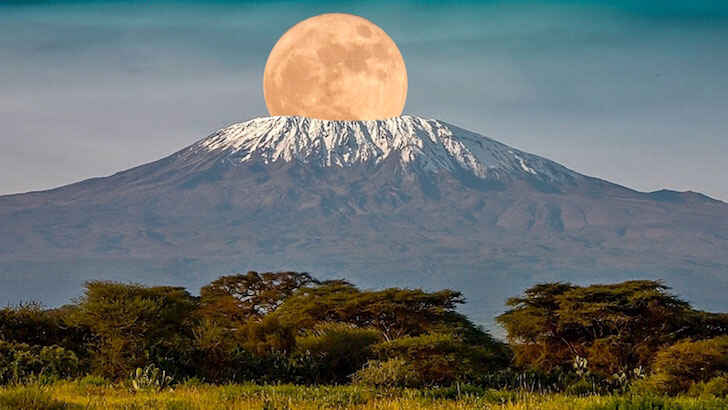

Mount Kilimanjaro is a dormant volcano located in Tanzania, in East Africa. It is the highest mountain in Africa, with a summit elevation of about 19,341 feet above sea level. The mountain is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, and Kilimanjaro is also an important water source for the region, with its glaciers and snowfields providing water for millions of people in the surrounding areas. The mountain is facing significant threats from climate change, with its glaciers melting at an alarming rate. It’s projected most ice will be gone by 2040.
Church of Nativity
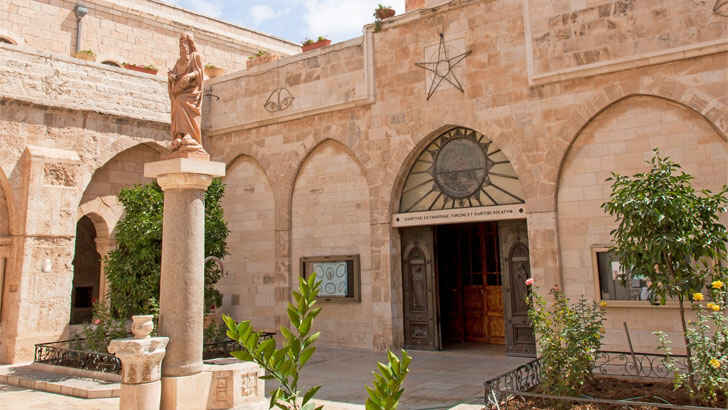

The Church of the Nativity is a major holy site for Christians, located in the city of Bethlehem in the West Bank. It is believed to be the birthplace of Jesus Christ and is one of the oldest continuously operating churches in the world. The Church of the Nativity was built in the 4th century AD, and is a fine example of Byzantine architecture,making it a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Unfortunately, water leaks are causing major damage to the wood and creating a fire hazard, putting the building and other historic artifacts in danger.
Everglades National Park
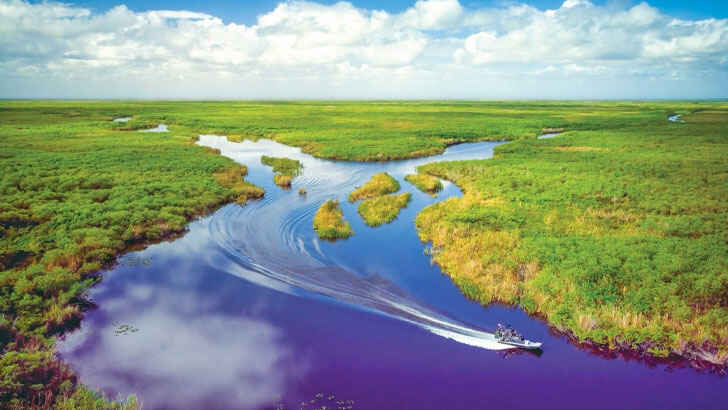

The Everglades National Park is a vast and diverse wetland ecosystem located in southern Florida. It is the third-largest national park in the lower 48 states and is home to a wide range of plant and animal life. The park is also an important water source for the region. The Everglades is facing significant threats from human activities, including development, pollution, and climate change, which have led to declines in the health and resilience of the ecosystem. Efforts are being made to protect and restore the Everglades, including the implementation of conservation measures and the expansion of protected areas.
Great Wall of China
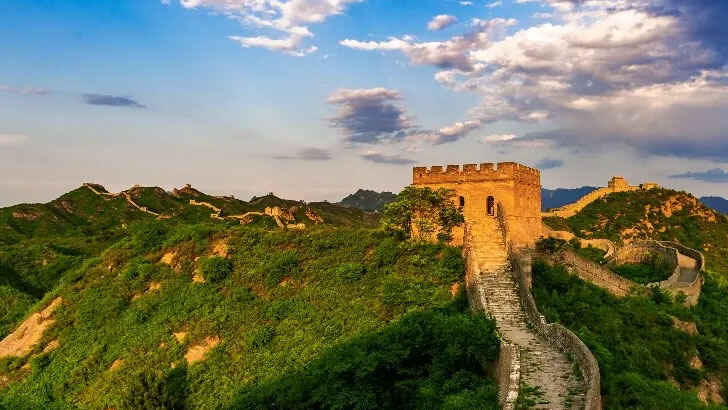

The Great Wall of China is a series of fortifications that were built, rebuilt, and maintained over the centuries to protect the Chinese Empire from invaders. The wall stretches over 13,000 miles and winds its way through mountains and deserts, making it the longest wall in the world. It was built over a period of more than 2,000 years, with the earliest sections dating back to the 7th century BC. The wall was constructed mainly of brick, tamped earth, and stone, and it was reinforced with watchtowers and defensive structures at regular intervals. However, erosion over the past few thousand years has allowed over 1,200 miles to deteriorate.
Seychelles
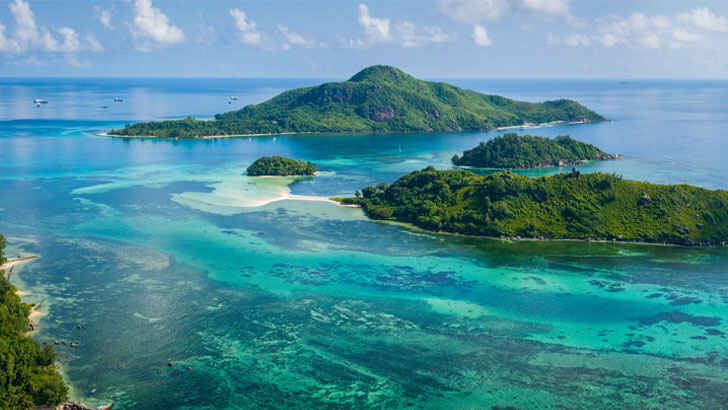

The Seychelles is a small archipelago of 115 islands located in the Indian Ocean, east of Africa. It is known for its stunning beaches, crystal clear waters, and lush vegetation, making it a popular destination for tourists seeking a tropical paradise. The Seychelles has a diverse array of ecosystems, including coral reefs, mangrove forests, and granitic islands, which support a wide variety of plant and animal life. The country is home to several protected areas, including national parks and marine reserves, however the destruction of the coral reef has resulted in the island beginning to erode away from once-subdued waves.
Glacier National Park
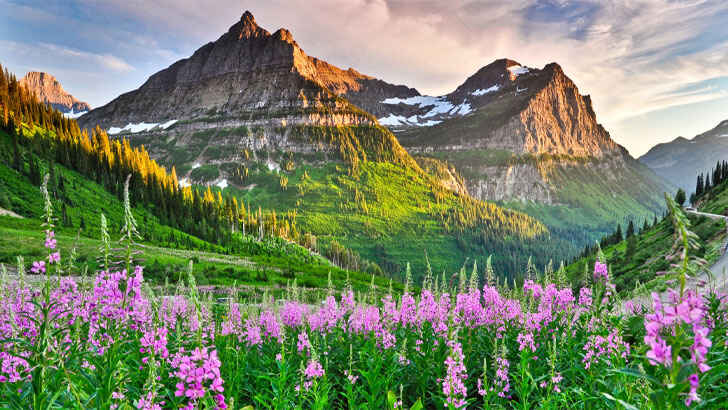

Glacier National Park is a protected wilderness area in the Rocky Mountains of Montana. It covers over 1 million acres of land and is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, including grizzly bears, wolves, mountain goats, and over 260 species of birds. The park is also home to some of the most spectacular scenery in the country, with towering peaks, deep valleys, and over 700 miles of trails that offer breathtaking views of the landscape. The park is a popular destination, but of the 150 glaciers that gave the park its name, only 26 remain due to global warming.
Machu Picchu
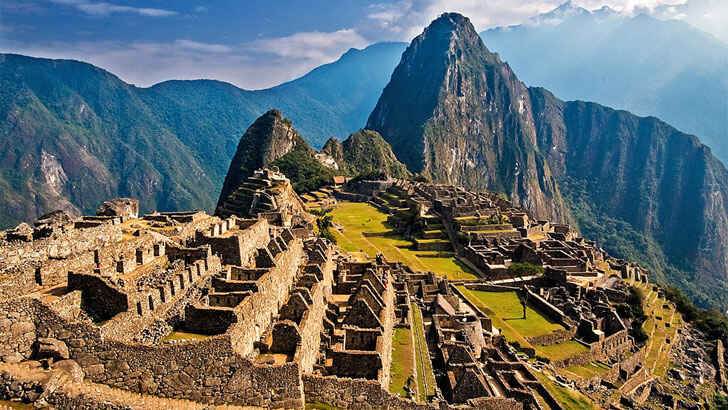

Machu Picchu is an ancient Inca citadel located in the Andes Mountains of Peru. It is a UNESCO World Heritage site and is considered one of the most important archaeological sites in South America. The site is believed to have been built in the 15th century and was abandoned just a few decades later, at the time of the Spanish conquest. Today, Machu Picchu is a popular tourist destination and is known for its stunning architecture and breathtaking views. However, tourism is bringing wear to the site, and it also sits on the Tambomachay fault, putting it at risk of a potential earthquake.
Old City of Jerusalem
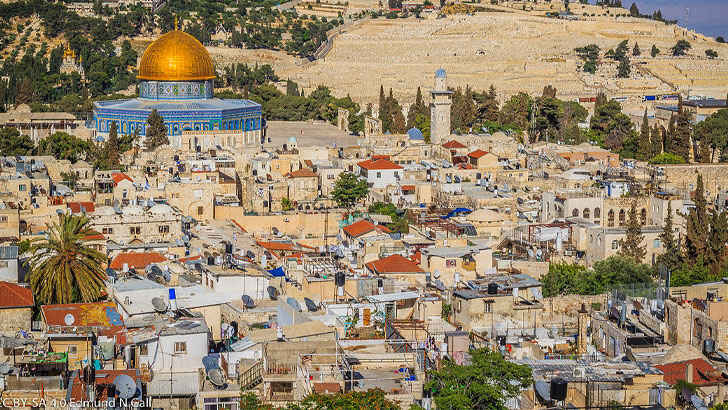

The Old City of Jerusalem is a historic neighborhood located in the heart of Jerusalem, Israel. It is a walled city that is divided into four quarters: the Jewish Quarter, the Christian Quarter, the Muslim Quarter, and the Armenian Quarter. The Old City is home to many of the city’s most important religious and historical sites, including the Western Wall, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, and the Dome of the Rock. However, it faces modern problems for being such a small area, like illegal construction, vandalism, and potential surrounding conflict.
Little Havana
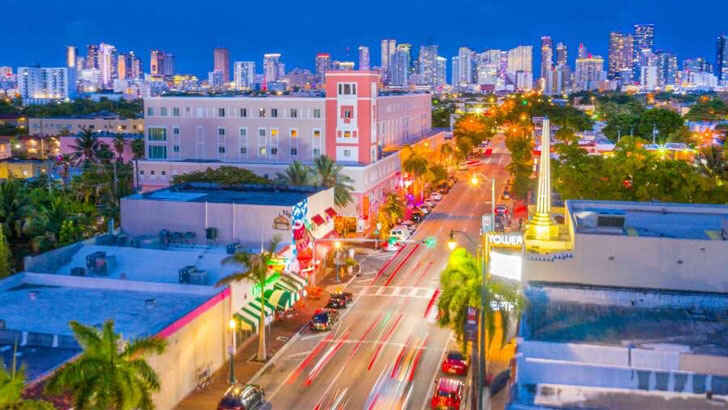

Little Havana is a neighborhood in Miami, Florida, known for its vibrant Cuban culture and history. Located just west of Downtown Miami, Little Havana is home to many Cuban immigrants and their descendants, who have contributed to the neighborhood’s lively atmosphere and colorful architecture. It’s a popular destination for tourists, who come to experience the neighborhood’s lively atmosphere and authentic Cuban culture. However, despite having historical significance, it’s main threat is building, as the bustling city continues to tear down and rebuild everywhere.
Borneo
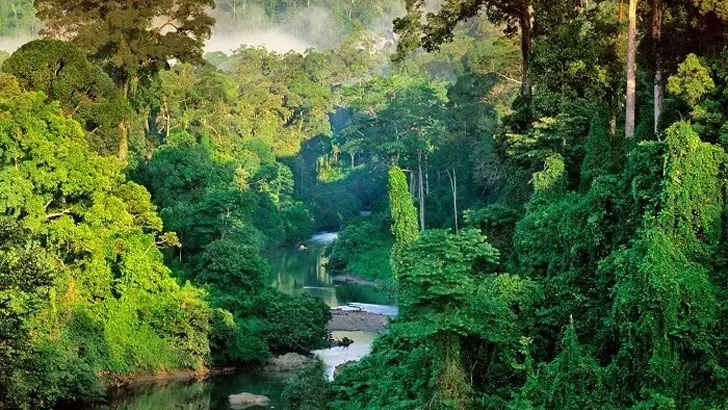

Borneo is the third-largest island in the world and is located in Southeast Asia. It is divided politically among three countries: Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei. Borneo is known for its diverse and abundant plant and animal life, and is home to a range of ecosystems, including rainforests, mangroves, and coral reefs. It is considered one of the most biodiverse regions on the planet. However, plantations, logging, fires, and poaching have all threatened the island, ruining its mystique and threatening all of its inhabitants.
Venice
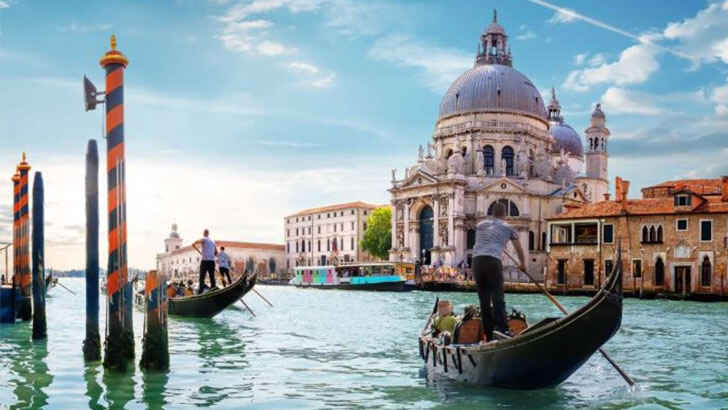

Venice is a city in northeastern Italy that is known for its network of canals, beautiful architecture, and rich cultural history. The city is built on a group of small islands in the Venetian Lagoon and is connected by over 400 bridges. Venice has a long history as a center of trade and culture, and it has been influenced by a variety of cultures over the centuries, including the Roman and Byzantine. Venice is a popular tourist destination, but maybe not for long, as the city’s water levels continue to rise, putting many buildings at flood risk. The tourism and added tour boats are only making matters worse.
Patagonian Ice Fields
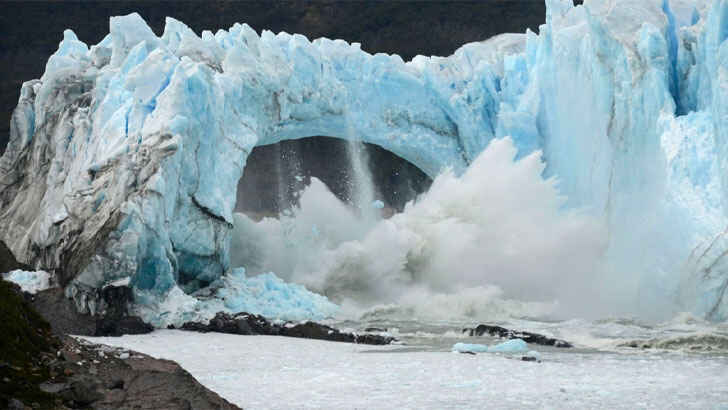

The Patagonian Ice Fields are a group of glaciers located in the Andes Mountains of South America. They cover an area of about 19,000 square miles and are the third-largest expanse of ice in the world, after Antarctica and the Arctic. The glaciers are home to a variety of plant and animal life, including penguins, seals, and several species of birds. The Patagonian Ice Fields are also a popular destination for tourists, who come to see the stunning landscape and to participate in outdoor activities. The ice fields are vulnerable to climate change and are losing mass at an alarming rate, leading to concerns about the future of the region’s freshwater supply.
Komodo Island
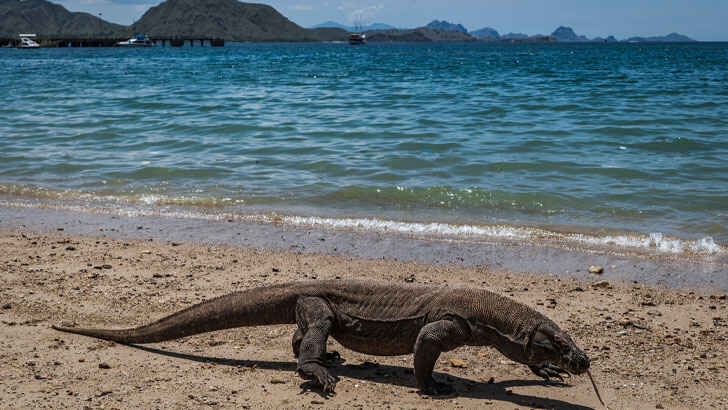

Komodo Island is a small Indonesian island located in the Lesser Sunda Islands. It is famous for being home to the Komodo dragon, the world’s largest living lizard. The island is part of the Komodo National Park, which was established in 1980 to protect the Komodo dragon and its habitat. In addition to the Komodo dragon, the island is also home to a variety of other species, including birds, deer, and wild pigs. The island has a unique ecosystem, with a dry, rocky landscape and a variety of plant life. Visitors to the island are largely to blame for making it more hostile to the environment there, and limitations to numbers of visitors are being discussed.
Micronesia
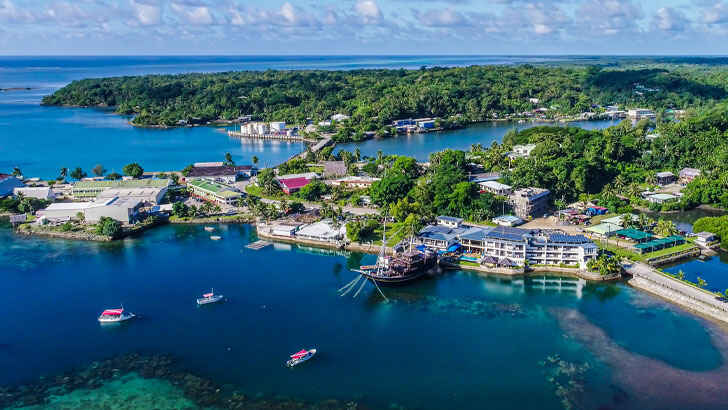

Micronesia is a region of the Pacific Ocean that consists of thousands of small islands, located north of Melanesia and east of the Philippines. The region has a diverse culture and history, with influences from various countries including Spain, Germany, Japan, and the United States. The region is known for its beaches, coral reefs, and clear blue waters, which make it a popular destination for diving and snorkeling. But since the economy of Micronesia is primarily based on tourism and the export of seafood, rising sea levels are threatening the island in more ways than one.
Acropolis
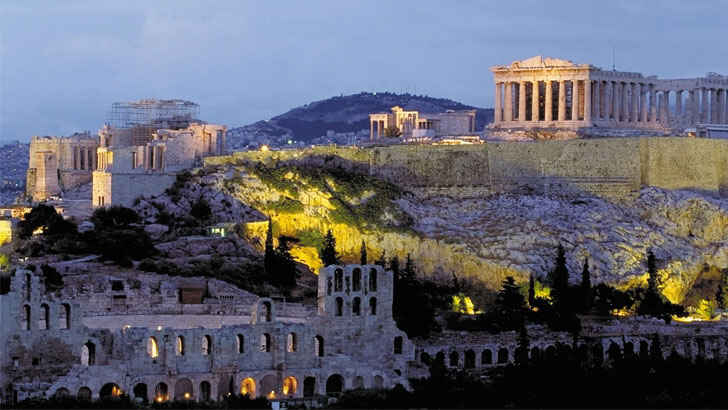

The Acropolis is a historic citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, Greece. It is one of the most famous landmarks in the world and is a symbol of Ancient Greek civilization. The Acropolis is home to several ancient temples and buildings, including the Parthenon, the Erechtheion, and the Temple of Athena Nike. These structures were built between the 5th and 4th centuries BCE and are considered some of the finest examples of Ancient Greek architecture. The Acropolis is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, but with increasingly decaying structures and more tourism only wearing down the center, its days are numbered.
Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City
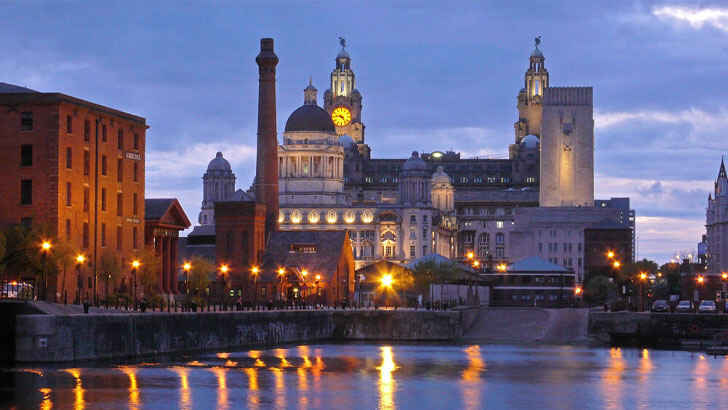

Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in the city of Liverpool, England. It is a designated area that includes several significant maritime and mercantile buildings and structures, as well as the historic waterfront of the city. The designation reflects Liverpool’s important role as a major port and center of trade and commerce during the 18th and 19th centuries. Liverpool Maritime Mercantile City is a popular tourist destination, with a variety of attractions and activities for visitors to enjoy, but modern city expansion and looming construction projects leave the future of this area up in the air.
The Door to Hell, Turkmenistan
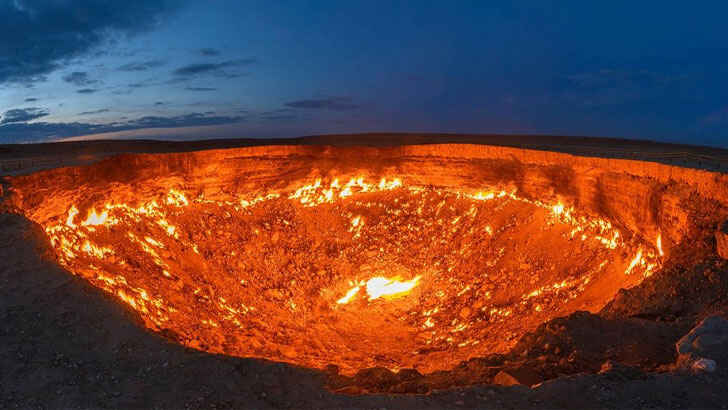

The Door to Hell is a natural gas field located in the Karakum Desert in Turkmenistan. It was a crater that measures approximately 230 feet in diameter and is known for its distinctive flaming gas emissions. It was formed in 1971 when a team of Soviet geologists accidentally caused a collapse of the surface while drilling for natural gas. In an effort to prevent the spread of methane gas, the geologists set the gas on fire, thinking that it would burn out quickly. However, the gas has continuously burned for more than 50 years, but the famed fire was officially commissioned to be put out in early 2022, meaning there’s literally days until it’s gone for good.
City of Potosí
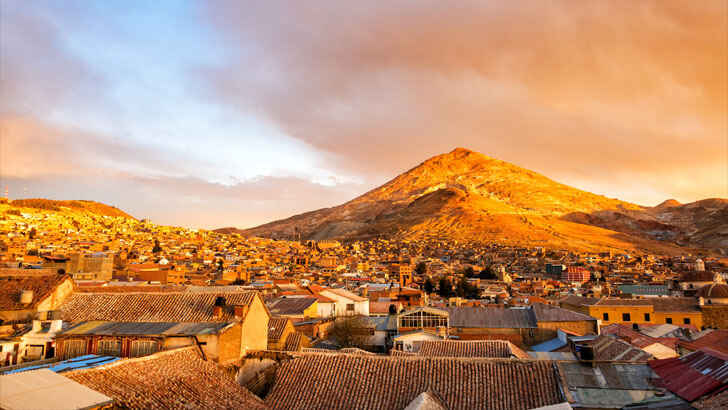

Potosi is a city located in the Bolivian Andes, at an altitude of 13,000 feet above sea level, that was founded in 1545 and was once one of the largest and wealthiest cities in the world, due to the vast silver deposits in the surrounding mountains. The silver mines of Potosi were a major source of wealth for the Spanish Empire and played a significant role in the global economy during the 16th and 17th centuries. Today, Potosi is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is known for its colonial-style architecture, and is also home to a vibrant indigenous culture. However, too much mining has made much of the city unstable physically, making it hazardous to live there.
European Alps
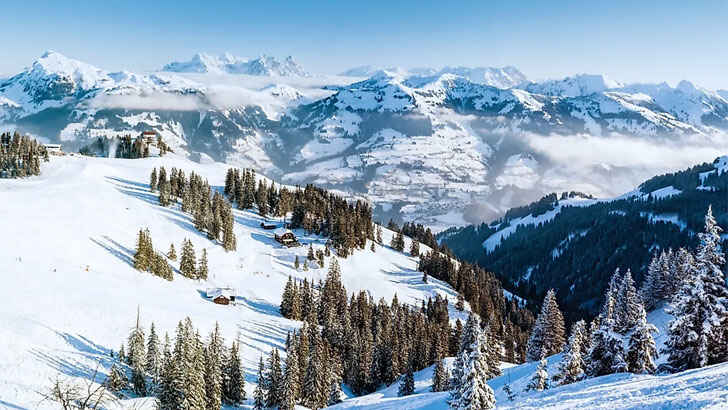

The European Alps are a mountain range located in central Europe, stretching across several countries including Austria, France, Germany, Italy, and Switzerland. The Alps are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, and are a popular destination for outdoor activities such as skiing and hiking. However, rising temperatures in the region have caused the loss of glaciers and a decline in snow cover, which could have serious consequences for local ecosystems and the economies that depend on winter tourism. In addition, the increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as storms and heatwaves are also causing problems for the region.
Tuvalu
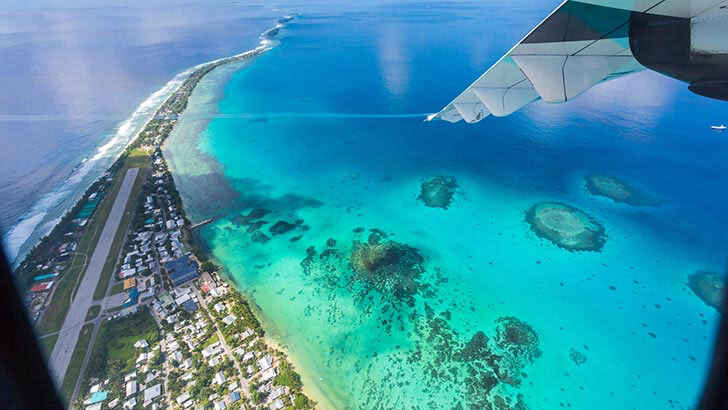

Tuvalu is a small island nation located in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Solomon Islands archipelago and is located to the east of Papua New Guinea. Tuvalu is known for its beautiful beaches and crystal clear waters, which make it a popular destination for snorkeling and diving. Tuvalu is home to a diverse range of plant and animal life, and the island’s economy is largely based on agriculture and tourism. Despite its small size and remote location, Tuvalu is an important cultural and historical site, but global warming and rising sea levels won’t spare it.
Bordeaux Vineyards
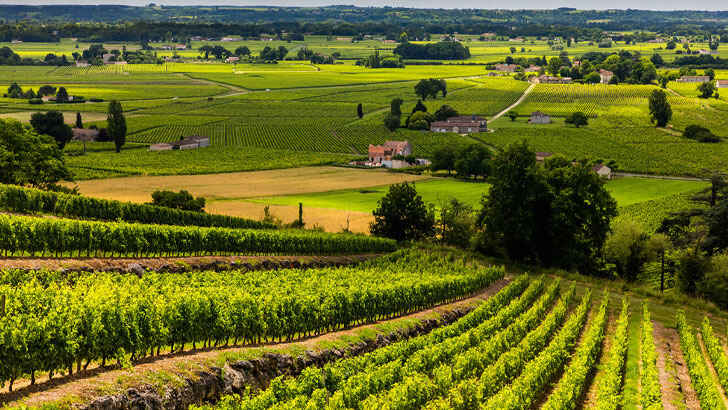

The Bordeaux region in southwestern France is home to some of the world’s most famous vineyards and wine-producing regions. The area is known for famous Bordeaux wines made from a blend of grape varieties such as Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, and Cabernet Franc. The Bordeaux region has a long and rich history of wine production, with roots dating back to Roman times. The region’s mild maritime climate, with cool winters and warm summers, is well-suited to grape growing, but with fluctuations in temperatures putting this precious climate at risk, the area may not be rich for wine making much longer.
Tikal
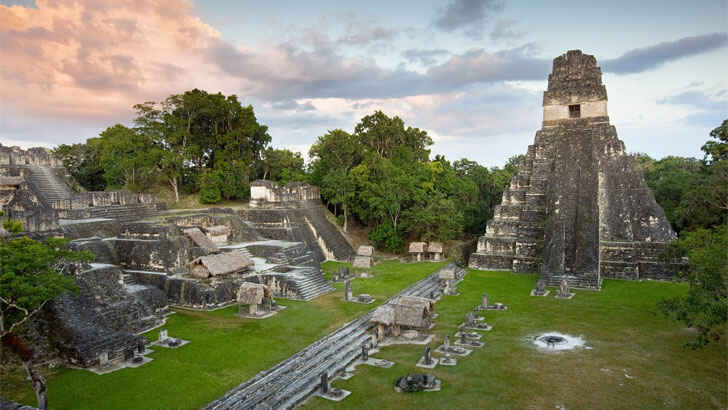

Tikal is an ancient Mayan city located in present-day Guatemala. It was one of the most important and influential cities of the Mayan civilization, and was a center of politics, religion, and trade. The city is best known for its impressive pyramids, temples, and other stone structures, which have been preserved and are now a popular tourist destination. The city was abandoned for hundreds of years after the collapse of the Mayan civilization, but was rediscovered in the 19th century. Now, as its limestone structure decays and visitors take pieces away, the city’s gone from untouched to tourist-torn.
Monteverde Cloud Forest
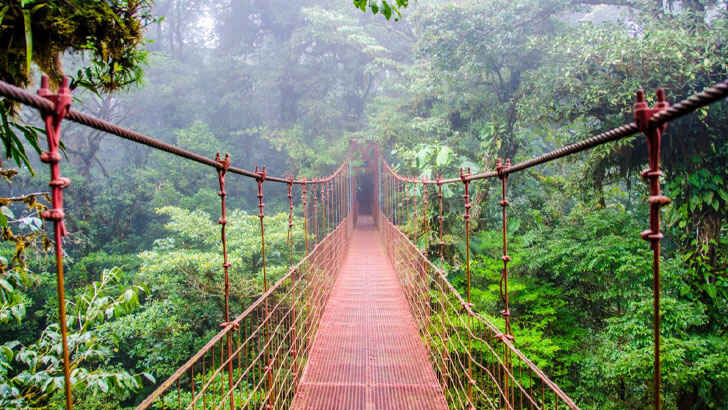

The Monteverde Cloud Forest is a unique and biologically diverse region located in the Cordillera de Tilarán mountain range in Costa Rica. The forest is named for its high altitude (around 4,600 feet above sea level) and the frequent clouds that cover the area, creating a misty and humid environment. The forest is home to more than 100 species of mammals, as well as over 400 species of birds and thousands of species of plants. And while the Monteverde Cloud Forest is an important site for conservation and scientific research, it’s very vulnerable to climate change and many plants and animals are being threatened with rising temperatures..
Maldives
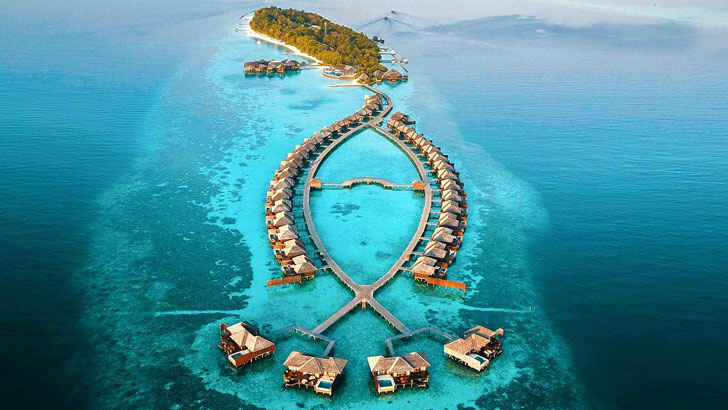

The Maldives is an archipelago of 26 coral atolls located in the Indian Ocean. It is a popular tourist destination known for its crystal clear waters, white sandy beaches, and luxury resorts. The Maldives is home to a diverse range of marine life, making it a popular destination for snorkeling and scuba diving. They have a tropical climate and are subject to monsoons, and since the country is made up of about 1,200 small coral islands, it’s the world’s lowest-lying country, and is vulnerable to the impacts of sea level rise. You can imagine the risk here.
Zahara de la Sierra
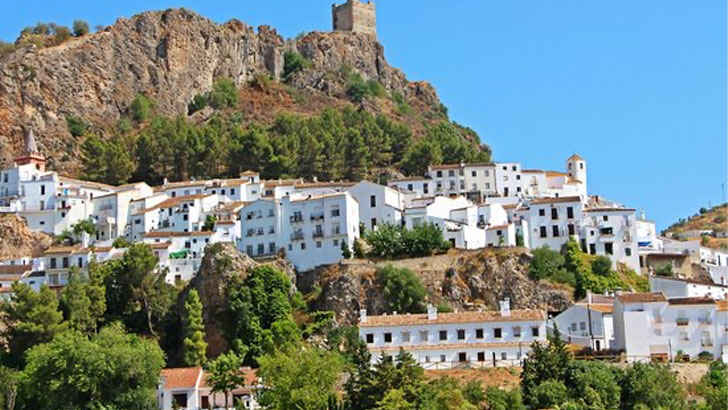

Zahara de la Sierra is a small town located in the province of Cádiz, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, in southwestern Spain. It is situated on a hill overlooking the Guadalete River and is known for its white houses and narrow streets. The town has a long history, with evidence of human settlement dating back to the Roman era. It was later conquered by the Moors and later by the Christians, and this history is reflected in the town’s architecture and culture. Today, Zahara de la Sierra is a popular tourist destination, but with rising rates of rainfall and temperature, the entire mountainside is at risk to lose its landscape.
Amazon Rainforest
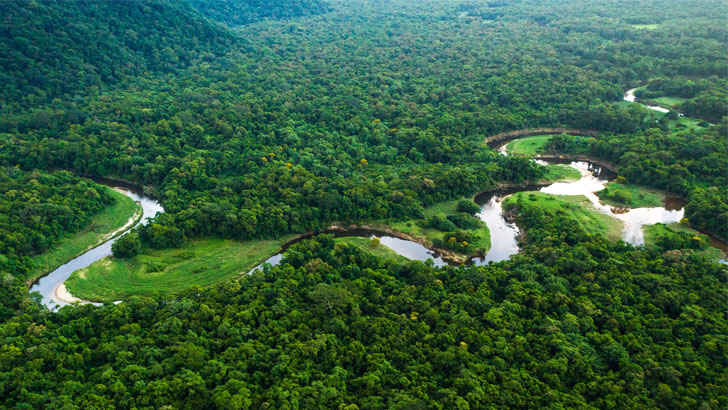

The Amazon rainforest, located in South America, is the largest tropical rainforest in the world and is home to an estimated 390 billion individual trees representing 16,000 species. It is also home to millions of people, including indigenous communities, and is an important source of oxygen for the planet. However, the Amazon rainforest is under threat due to deforestation, and the destruction of the Amazon rainforest also has significant consequences for the global climate, as the forest plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s temperature and weather patterns. It’s imperative that we protect the rainforest at all costs, and if we don’t, all of humanity will pay the consequences.
Galapagos Islands
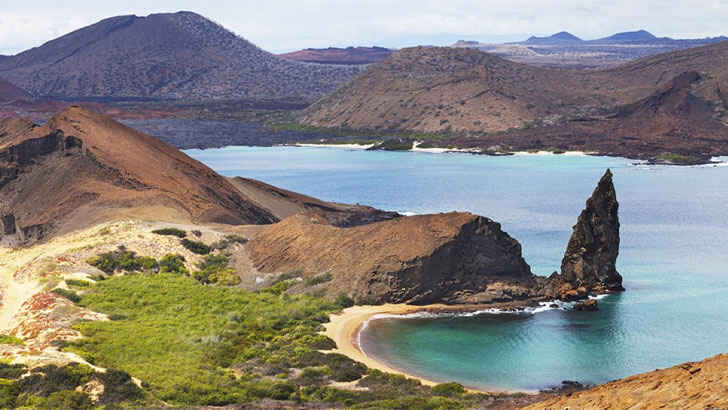

The Galapagos Islands are a group of volcanic islands located in the Pacific Ocean, about 620 miles west of Ecuador. The Galapagos are known for their unique and iconic species such as giant tortoises, marine iguanas, and blue-footed boobies, and the islands are also home to a variety of ecosystems, including dry and humid forests, grasslands, and rocky coasts. The Galapagos were made famous by naturalist Charles Darwin, and today, they are a popular tourist destination and are also protected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. But like many other tropical destinations, tourism and climate change are putting the Galapagos in serious threat due to overpopulation.
Congo Basin
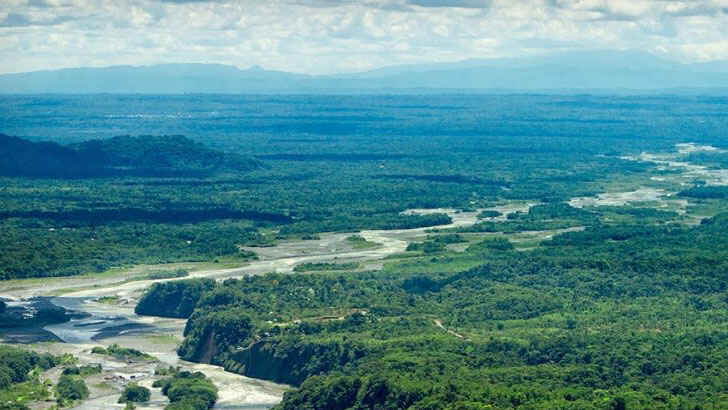

The Congo Basin is a large region in central Africa that is home to the second-largest rainforest in the world, after the Amazon. The Congo Basin covers an area of approximately 1.4 million square miles, and is home to a diverse range of plant and animal species. The Congo Basin is home to a variety of ecosystems, including dense tropical forests, swamps, and savannas, and it’s also home to millions of people, including indigenous communities who have lived in the region for centuries. The Congo Basin rainforest is under threat from a variety of human activities, including deforestation, mining, and the expansion of agriculture. Unfortunately, if not stopped soon, it could see catastrophic consequences by 2040.
Yangtze River Basin
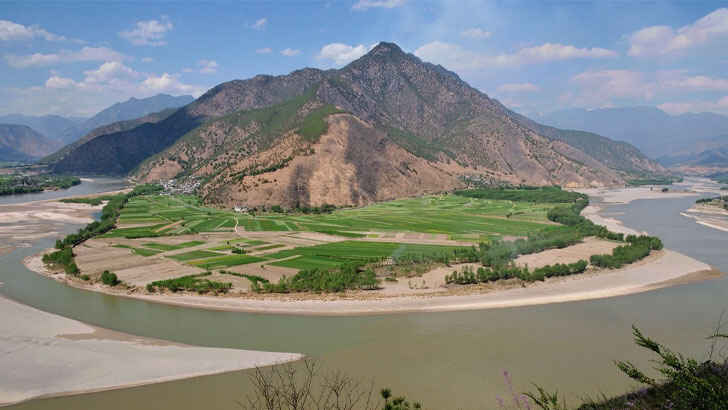

The Yangtze River Basin is the largest river basin in China and is home to over 400 million people. The Yangtze River, which is the longest river in Asia, runs through the basin and is an important source of water, food, and transportation for the region. The region is known for its rich culture and history, and it is an important economic hub for China. However, the Yangtze River Basin is facing a number of challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and the construction of large hydroelectric dams.
Olympia
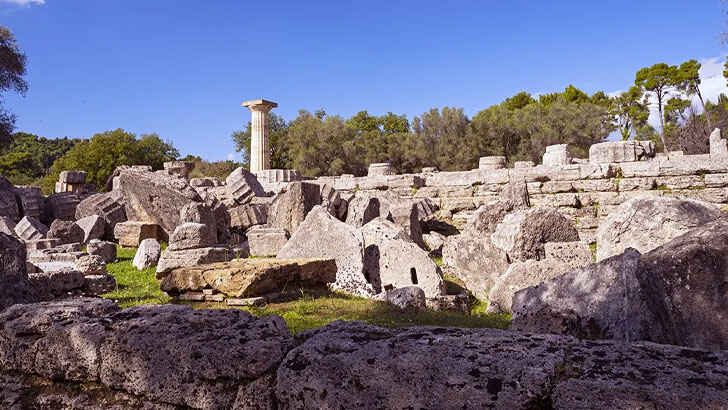

Olympia is an ancient city located in the western part of the Peloponnese region in Greece. It is best known as the site of the Olympic Games, which were held every four years in honor of the Greek god Zeus. The site of ancient Olympia includes the Temple of Zeus, the Temple of Hera, and the stadium where the games were held. It is a popular tourist destination and is also protected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. But like many ancient cities, preservation has become tough and many of the old sites were built before materials improved, and the high volume of tourism is taking its toll.
The Sundarbans
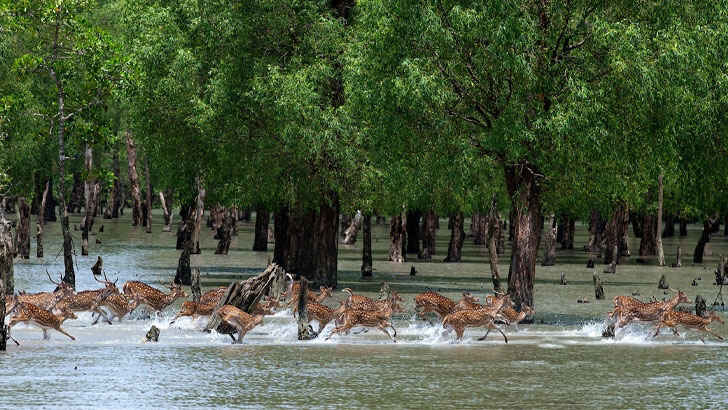

The Sundarbans is a vast mangrove forest located in the delta region of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers in Bangladesh and India. It is the largest mangrove forest in the world and is known for its Bengal tigers, which are an endangered species that are found nowhere else in the world. It is also an important carbon sink, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. The Sundarbans is protected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, but conservation efforts may not be enough to save the region from poaching, deforestation, and other industry hurting the species there.
Salar de Uyuni
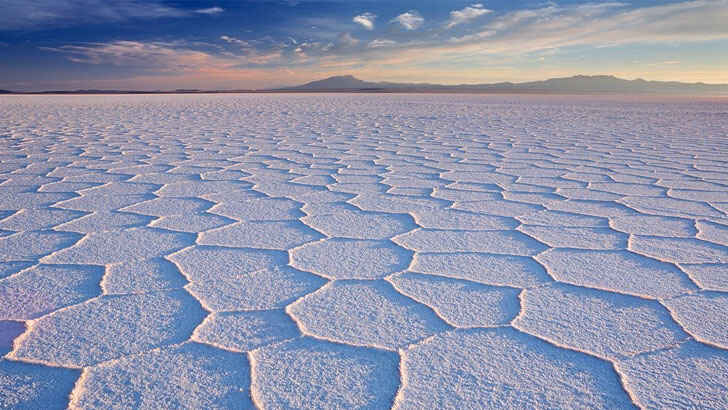

Salar de Uyuni is a vast salt flat located in the Andes mountains of southwestern Bolivia. It is the largest salt flat in the world and covers an area of over 3,900 square miles. It’s the result of a prehistoric lake that dried up, leaving behind a layer of salt that is several meters thick in some places. It is also an important habitat for a number of threatened and endangered species, including the Andean flamingo and the puna ibis. Salar de Uyuni is protected as a national park and is a popular destination for tourists who want to experience its unique landscape and wildlife, but because it’s on top of approximately half of the world’s lithium reserves, mining could make it a destination of the past.
Joshua Tree
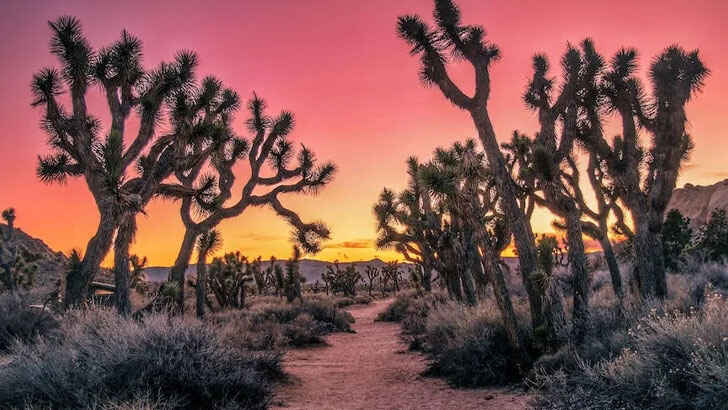

Joshua tree is a species of tree that is native to the Mojave Desert in the southwestern United States. It is known for its distinctive, spiky leaves and its ability to survive in harsh, dry environments. Joshua trees are an important part of the desert ecosystem and provide habitat for a number of species of birds and animals.Rising temperatures and decreasing rainfall in the Mojave Desert are making it harder for Joshua trees to survive. The trees are also threatened by increasing frequency and severity of wildfires, which can damage or destroy the trees. In addition, Joshua trees are being affected by the expansion of urban areas, as well as by recreational activities such as off-road vehicle use.
Choquequirao Archaeological Park
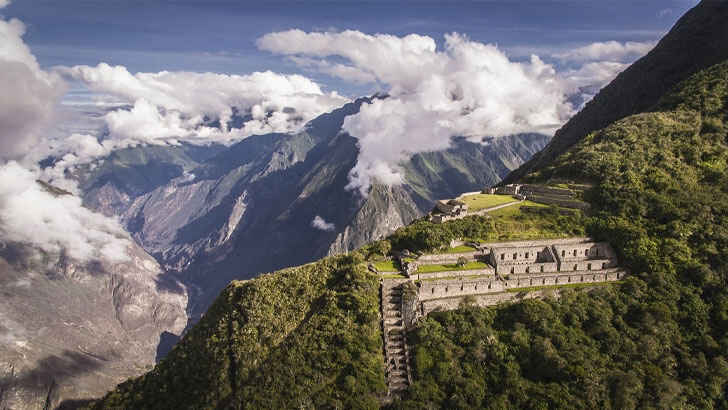

Choquequirao Park is a protected area located in the Andes mountains of Peru. It is home to the Choquequirao Archaeological Site, which is an ancient Inca city that was built in the 15th century. The site is known for its impressive stone terraces, plazas, and buildings, which were built using traditional Inca construction techniques. Choquequirao Park is also home to threatened and endangered species such as the Andean condor and the mountain tapir. The park is a popular destination for hikers and adventure travelers, and though it’s protected by the Peruvian government, increased volumes in visitors similar to Machu Picchu threaten the ruins.
Alaskan Tundra
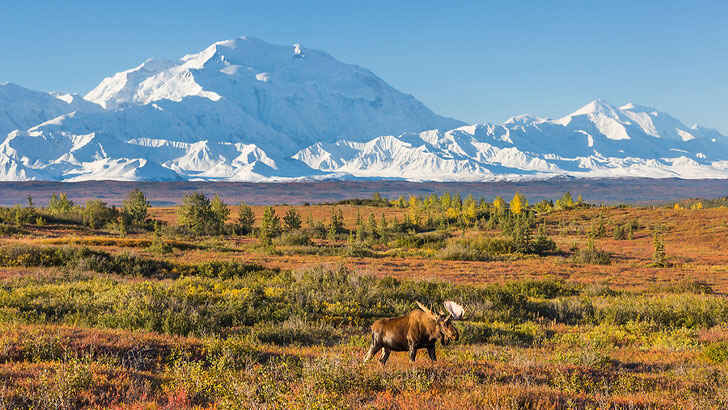

The Alaskan tundra is a vast region of Arctic land located in the northernmost part of the state. It is characterized by its cold, harsh climate, with temperatures that can reach as low as -40°F in the winter. However, the Alaskan tundra is facing a number of challenges due to climate change. Rising temperatures in the region are causing the permafrost to thaw, leading to the loss of habitat for some species. The tundra is also experiencing longer and more frequent wildfires, which can damage or destroy the plants and animals that live there. In addition, the tundra is being affected by the melting of sea ice, which is disrupting the migration patterns of marine mammals such as polar bears and seals.
Sub-Saharan Africa
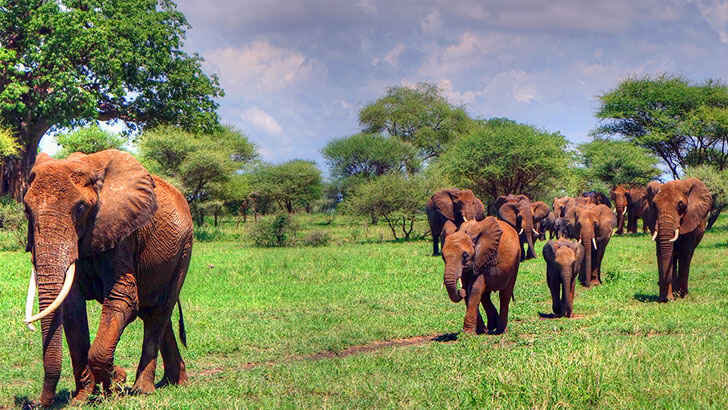

Sub-Saharan Africa is a large region located south of the Sahara Desert in Africa. It is home to a diverse range of cultures, languages, and ecosystems, and is an important source of food, water, and other resources for the global community. However, Sub-Saharan Africa is also one of the regions of the world that is most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns in the region are affecting the availability of water and the productivity of crops, leading to food insecurity and economic challenges. Sub-Saharan Africa is also experiencing more frequent and severe natural disasters such as droughts, floods, and cyclones, which can have devastating consequences for the people who live there.
Egyptian Pyramids
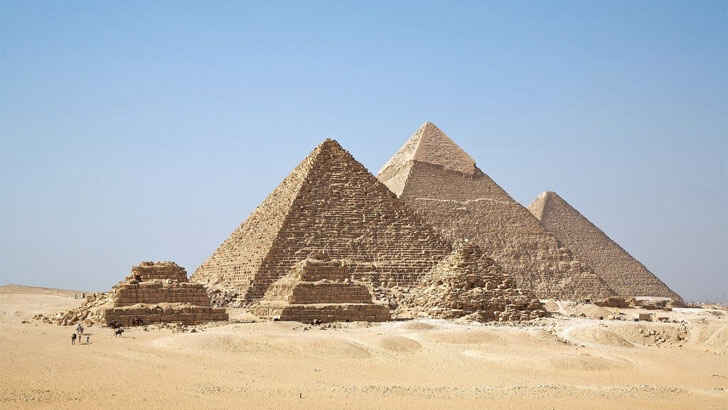

The Egyptian pyramids are a series of ancient tombs and burial structures located in Egypt. The most famous pyramids are the Great Pyramid of Giza, which is the oldest and largest of the pyramids and is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The pyramids were built using large blocks of stone, and the structures have survived for thousands of years due to their strong foundations and the dry desert climate. However, the pyramids are also facing a number of challenges, including damage from pollution, vandalism, and the effects of tourism. Rising groundwater and sewage could eventually destabilize the ancient structures.
Outer Banks
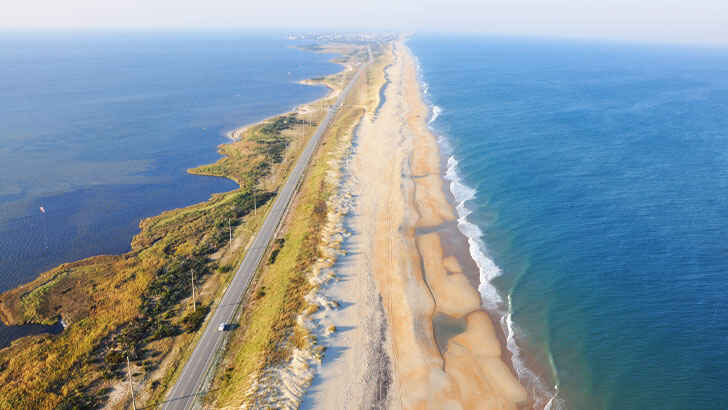

The Outer Banks is a string of barrier islands located along the coast of North Carolina, in the southeastern United States. It is known for its beautiful beaches, rich history, and diverse ecosystem. The Outer Banks is home to a number of protected areas, including the Cape Hatteras National Seashore and the Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge. However, rising sea levels and increasing frequency and intensity of storms are threatening the stability of the islands. In addition to damaging infrastructure and disrupting the local economy, 6 feet of estimated erosion a year is being lost from the islands.
More From Bon Voyaged
-


TV And Movie Roles That Were Recast
-


20 Countries And The Most Popular Soft Drink According To…
-


Famous Scripted Reality TV Shows
-


Celebrities We’ve Lost Recently
-


The Trump Family Tree Of Gold
-

Ironic, Clever, And Hilarious Answers To Test Questions
-


25 Reasons Why A Vacation Can Make Or Break A…
-


Camping Fails That Make You Want To Stay Home
-


Unusual Rules The Amish Have To Follow
-

Top American Colleges To Avoid
-


Unsolved Scientific Mysteries From History
-


Can You Name These Historical Figures?

